| ☰ See All Chapters |
How to return HTTP status codes from spring Controllers - @ResponseStatus Annotation
When you want specify the response status of any controller method you can use @ResponseStatus annotation with that method. By default, for a successful response spring provides an HTTP 200 (OK) response, still if you want to change the response status you can use @ResponseStatus annotation.
@ResponseStatus is generally used to change response status of error message response. @ResponseStatus annotation can be used with Exception handling method (methods annotated with @ExceptionHandler) or with exception class. Let us see an example on how we can use @ResponseStatus annotation with exception class.
Example for @ ResponseStatus annotation
pom.xml
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.java4coding</groupId> <artifactId>ResponseStatus_WithSpringBoot</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>ResponseStatus_WithSpringBoot</name> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.6.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> </project> |
DemoController.java
package com.java4coding;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController public class DemoController {
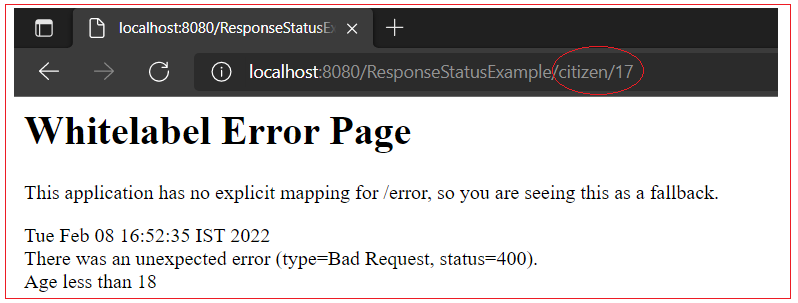
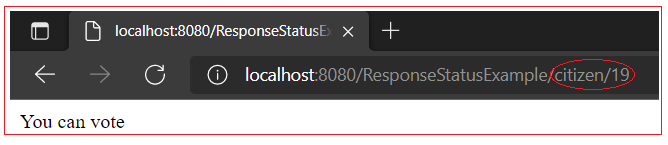
@RequestMapping(value = "/citizen/{age}") public String sayHello(@PathVariable("age") long age) { if (age < 18 ) {
throw new AgeNotAllowed("You are not allowed for voting"); } return "You can vote"; }
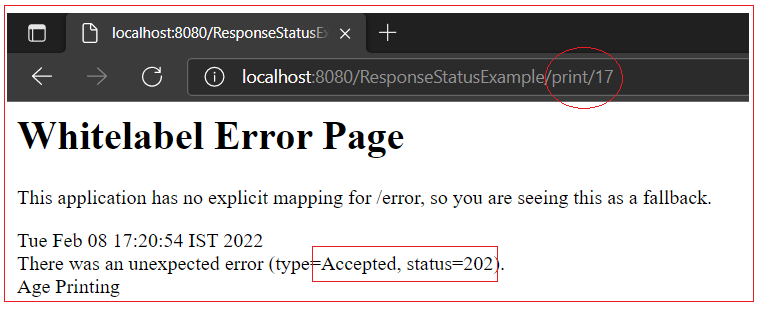
@RequestMapping(value = "/print/{age}") @ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.ACCEPTED, reason = "Age Printing") public String printAge(@PathVariable("age") long age) { return "Your age is" + age; } } |
AgeNotAllowed.java
package com.java4coding;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, reason = "Age less than 18") public class AgeNotAllowed extends RuntimeException {
public AgeNotAllowed(String message) {
super(message); } }
|
SpringBootDemo.java
package com.java4coding;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo.class, args); } } |
application.properties
# Applicationn context name server.contextPath=/ExceptionHandler |
Project Directory Structure
Output
All Chapters

